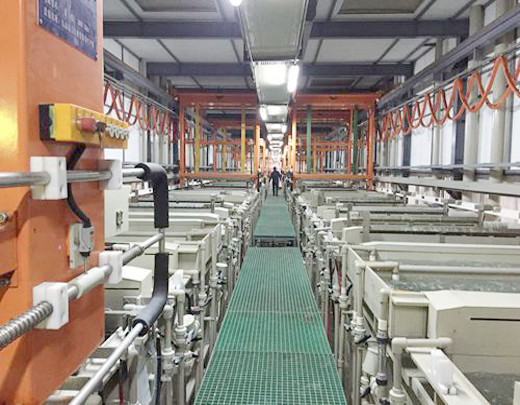
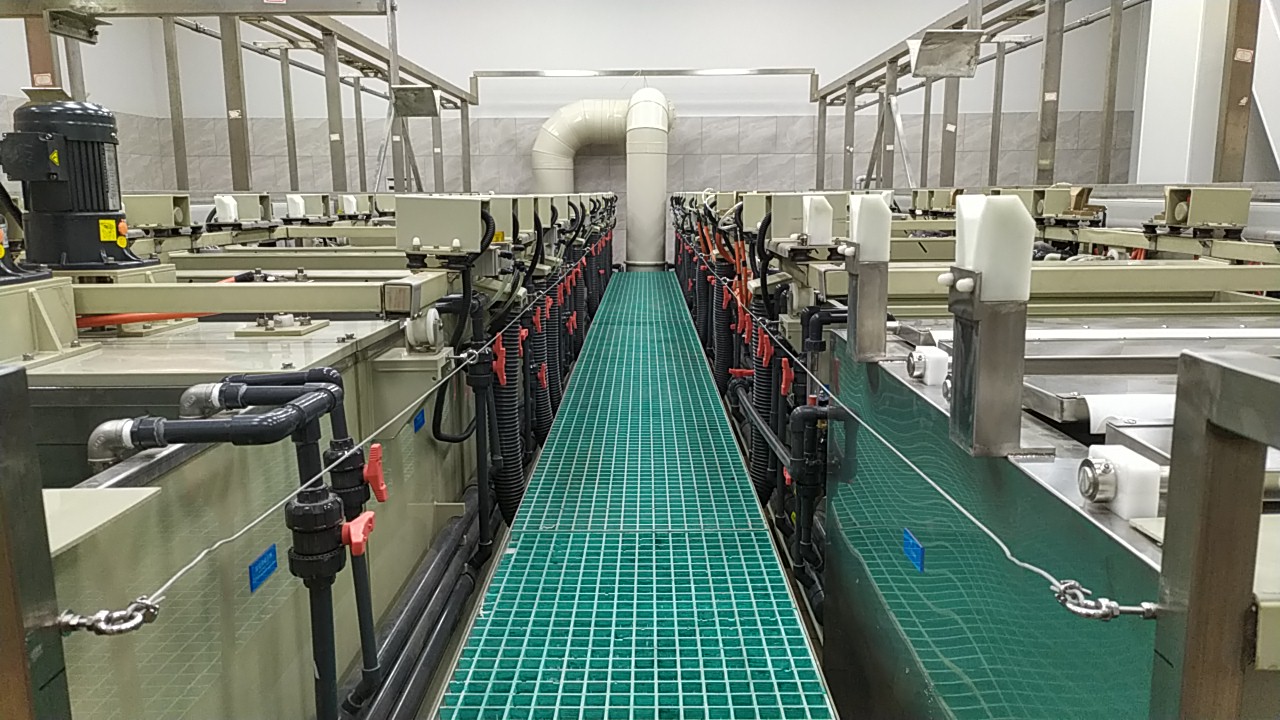
Zinc alloy is widely used in bathroom, luggage, and footwear accessories due to its convenient molding, strong plasticity, low cost, and high processing efficiency. However, the foaming problem of zinc alloy (electroplating; spraying) has always troubled friends from hardware and electroplating factories.
Today, we will compile the experience of zinc alloy foaming from multiple hardware and electroplating factories that we have served, including the following aspects:
1.At the beginning of the design of zinc alloy products, it is necessary to consider the settings of the feeding and slag discharge ports and exhaust ports of the mold. Because the flow channels of the workpiece for feeding and slag discharge are smooth and free of air, water stains, and dark bubbles, which directly affect whether the subsequent electroplating is bubbling, the qualified feeding and slag discharge molds cast the workpiece with a smooth, white, and no water stains on the surface.
2.In the development of molds, it is also necessary to consider the tonnage and pressure of the molding machine. We have personally experienced a 20-30% foaming event after zinc alloy electroplating. A friend of a hardware factory received a large order of several million yuan, and eight molds were opened. The pressure was insufficient, and the exhaust was poor. No matter how to solve the problem before electroplating, 20-30% of the molds were blistered. Finally, four molds were blocked, and four the first mock examination was replaced by four molds. After electroplating, there was no blister.
3.The polishing solution, polishing paste, and oxide layer on the pre-treatment surface are not treated thoroughly, and there is often rolling. The workpiece after rolling and polishing has a bright surface; Many employees in the pickling process of electroplating factories simply acid wash, resulting in the surface adhesion of the polishing agent not being cleaned, often resulting in foaming. In addition, the polishing agents used by the polishing plant are also closely related, and some of the surfactants in the polishing agents are extremely difficult to remove.
4.Before the product enters the alkaline copper (commonly known as copper bottom by many hardware enthusiasts) plating bath, there is still an oxide film (acid washed film) on the surface of the workpiece. The wax and oil removal film has not been completely treated with black film. So removing the film is crucial. In the early years, anti staining salt could still be used to remove it. Currently, environmental protection does not allow the discharge of wastewater containing anti staining salt. It is recommended to use LJ-D009 film removal powder, which has better effect than anti staining salt and can also remove the nickel layer. The COD discharge meets international standards
5.Alkali copper plating tank contains organic matter with many impurities, and free cyanide is not within the range. Analyze the composition of the alkali copper cylinder to see if sodium cyanide is low or sodium hydroxide is high! If adding a brightener, be careful. The brightener is too high, and the cleaning of the alkaline copper cylinder is crucial. It is recommended to treat it with carbon every 3-5 days
6.The conductivity of the alkaline copper cylinder is also important. Whether the anode dissolves normally and whether the anode copper plate is sufficient will lead to foaming
7.Zinc alloy products blister after coming out of the oven; It may be due to uneven temperature in the oven, which means the temperature is too high. Due to the lack of tightness during die-casting, acid can easily enter the water stains and sand holes of zinc alloy. Even with surface coatings, acid and zinc will still undergo chemical reactions, producing a large amount of hydrogen gas. When the air pressure inside is higher than atmospheric pressure to a certain extent, combined with high temperature, bubbles will be generated







 Nov. 09, 2021
Nov. 09, 2021