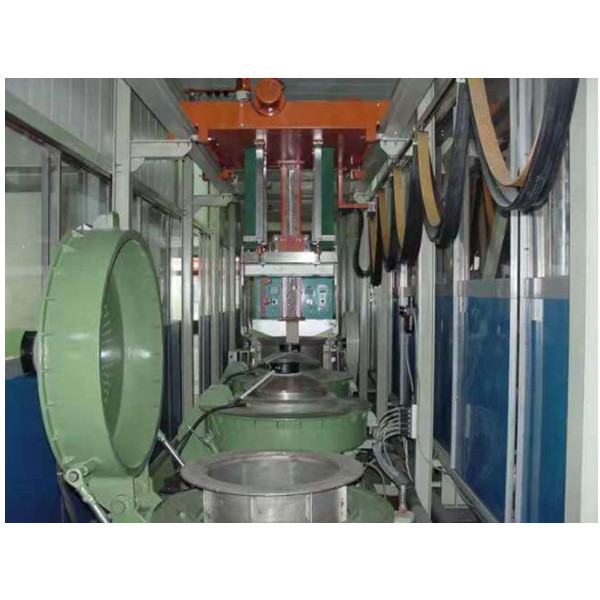
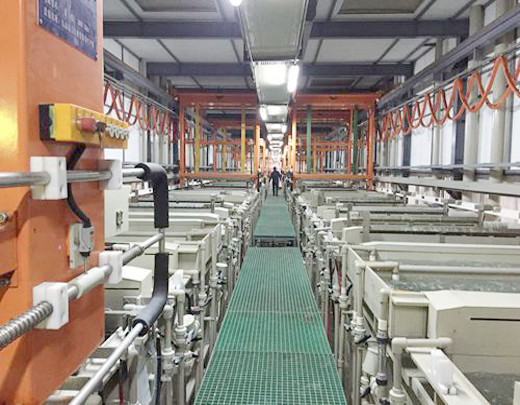
To master and manage the degreasing process, we must correctly grasp the principle of the combination of coating and metal substrate.This point is often ignored, which brings difficulties to practice.
Relevant data point out that the mechanical bonding caused by the micro unevenness of the surface of the coating and the substrate can be firm only when the intermolecular and intermetallic forces are combined between the coating and the metal body, and the intermolecular and intermetallic forces can be shown only in a very small distance.
When the distance between molecules exceeds 5μM, the intermolecular force does not work.Therefore, there is a thin degreasing film and oxide film on the surface of the matrix, which can also hinder the adhesion between molecules or metals.
In order to achieve the above combination, it is necessary to completely remove the degreasing stain, rust and scale on the products.By “quite thorough”, we do not mean that the surface is required to be absolutely clean after pretreatment, but only qualified surface. The so-called qualified surface actually means that the film that hinders electroplating after pretreatment must be removed and replaced by a film suitable for easy electroplating.
At the same time, the metal surface shall be absolutely flat through pre plating treatment. After mechanical treatment such as polishing, polishing or rolling, sand blasting, the surface shall be removed of obvious scratches, burrs and other defects, so that the substrate surface meets the substrate leveling and finish requirements of the plated parts, and then the degreasing and rust shall be removed.
This point must be clear. Only when this point is clear can the process flow and formula of pre plating treatment be selected correctly and in combination with the actual situation in the same formula of pre plating treatment.
How to apply degreasing process in production?
Alkaline degreasing is usually used.The degreasing removal fluid composition and process conditions are selected according to the degreasing contamination state and the type of metal materials.
When there is a large amount of grease on the surface, that is, the degreasing layer is very thick, greasy and sticky, it can not be easily removed by alkali only. Other methods must be used first, such as brushing solvent for degreasing removal, and then alkaline degreasing removal after pretreatment. Alkaline degreasing removal fluid is strongly alkaline.It reacts with some metals to cause obvious corrosion.
Therefore, the degreasing of aluminum zinc plated parts should be carried out under low temperature and low alkali conditions as far as possible. It is generally possible to treat steel parts with high alkalinity, but when dealing with non-ferrous metal parts, the pH of the degreasing solution should be adjusted to an appropriate range.For example, the pH of aluminum, zinc and their alloys shall be controlled below 11, and the degreasing removal time of such products shall not exceed 3min.
In terms of cost, some advocate low-temperature degreasing removal, but reducing the temperature is contradictory to improving the efficiency. The higher the temperature, the faster the physicochemical reaction between the degreasing adhered to the surface and the cleaning agent, and the easier the degreasing removal.
Practice has proved that the viscosity of degreasing stain decreases with the increase of temperature, so it is easy to remove degreasing, but low temperature has no such effect.Therefore, considering the use of emulsifier and surfactant, whether it is good to remove degreasing at high temperature and what temperature is appropriate to control, the author’s experience is that it is better to control at 70 ~ 80 ℃, which can also help to eliminate the residual stress of the base metal due to machining and improve the adhesion between the coating, especially multi-layer nickel.
General Iron and steel parts can adopt combined degreasing, such as cathode degreasing for 3 ~ 5min and then anode degreasing for 1 ~ 2min, or anode degreasing for 3 ~ 5min and then cathode degreasing for 1 ~ 2min. This can be realized by twice degreasing or power supply with reversing device.
For high-strength steel, spring steel and thin parts, in order to prevent hydrogen embrittlement, only anodic degreasing for a few minutes.However, for non-ferrous metal parts such as copper and copper alloy, anode degreasing is not allowed, and only cathode degreasing can be used for 1 ~ 2min.
In the preparation and maintenance of degreasing solution.The preparation of chemical degreasing removal and electrolytic degreasing removal solutions is relatively simple.First dissolve other materials except surfactants with 2 / 3 of the bath volume of water and stir at the same time (to prevent drug caking). Because these drug materials release heat when dissolved, there is no need to heat up. The surfactant should be dissolved in hot water before adding. If it cannot be dissolved at one time, pour out the upper clear liquid, add water to dissolve, add it to the specified volume and mix well.
Attention shall be paid to the management of degreasing fluid:
① Test the supplementary materials regularly, and add 1 / 3 ~ 1 / 2 of the original dosage of surfactant every week or half a month according to the production volume.
② The iron plate used shall not contain too many heavy metal impurities to prevent them from being brought into the coating. The current density shall be maintained at 5 ~ 10A / DM2, which shall be selected to ensure sufficient bubbles.This ensures that the degreasing beads are mechanically torn off the electrode surface and the solution can be stirred.When the degreasing stain on the surface is constant, the greater the current density, the faster the degreasing removal speed.
③ The degreasing floating in the bath shall be removed in time.
④ Clean the sludge and dirt in the bath regularly and replace the bath liquid in time.
⑤ Low foam surfactant shall be selected as far as possible in the electrolyte, otherwise the quality will be affected when it is brought into the electroplating bath.
How to master and manage the acid etching (pickling) process?
Like the degreasing process, acid etching (pickling) plays an important role in pre plating treatment. The two cooperate with each other and are applied in the production of pre plating treatment. Its main purpose is to remove the rust and oxide scale of metal plating products.
Generally, the removal of a large number of oxides is called strong etching, and the removal of thin oxide films that are difficult to be detected by the naked eye is called weak etching, which can be divided into chemical etching and electrochemical etching.Weak etching is used for the last treatment process after strong etching, that is, before the workpiece enters the electroplating process. It is a metal surface activation process, which is easy to be ignored in production, which is one of the reasons for electroplating peeling.
If the weak etching solution is one of the components in the next plating solution, or its introduction will not affect the plating solution, it is best to directly enter the activated plating part into the plating bath without cleaning.
For example, for the dilute acid activation solution used before nickel plating, in order to ensure the smooth progress of the etching process, the degreasing must be removed before etching, otherwise, the acid and metal oxides will not be in good contact, and the chemical dissolution reaction will be difficult.
Therefore, to master acid etching, we must also understand these basic principles theoretically.
Generally, sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid are mainly used for removing oxide scale of iron and steel parts. The method is simple, but it is difficult to achieve the expected purpose without paying attention in actual production.
The selection standard of sulfuric acid etching process conditions is usually identified by the appearance of the workpiece after pickling based on experience, which can not be controlled quantitatively after all.Practice has proved that the scale removal effect at 40 ℃ is much greater than that at 20 ℃, but the stripping effect is not increased in proportion with the further increase of temperature.
At the same time, in sulfuric acid with concentration lower than 20%, the acid etching speed increases with the increase of concentration, but decreases when the concentration exceeds 20%.Therefore, it is considered that the standard process conditions of sulfuric acid concentration of 10% ~ 20% and etching below 60 ℃ are more suitable.It should also be noted that the aging degree of sulfuric acid solution. Generally, when the iron content in the acid washing solution exceeds 80g / L and the ferrous sulfate content exceeds 2.5g/l, the sulfuric acid solution can not be reused.
At this time, the solution shall be cooled to remove the excessive ferrous sulfate crystallization, and then new acid shall be added until the process requirements.
The selection standard of acid etching process conditions of hydrochloric acid should generally be controlled at 10% ~ 20% and carried out at room temperature.Compared with sulfuric acid, under the same concentration and temperature, the etching speed of hydrochloric acid is 1.5 ~ 2 times faster than that of sulfuric acid.
Whether sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid should be selected for acid etching depends on the specific situation of actual production. For example, sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid are commonly used in strong etching of ferrous metals, or the “mixed acid” mixed with the two in a certain proportion.
However, what kind of acid is selected for chemical strong etching depends on the composition and structure of oxides on the surface of iron and steel parts.At the same time, the etching speed should be fast, the production cost should be low, and the size deformation and hydrogen permeation of metal products should not occur as far as possible. However, it must be understood that the removal of oxide scale in hydrochloric acid mainly depends on the chemical dissolution of hydrochloric acid, and the mechanical stripping effect of hydrogen is much smaller than that in sulfuric acid,When hydrochloric acid is used alone, the acid consumption is larger than that when sulfuric acid is used alone.
When the rust and oxide scale on the surface of the plated part contain more oxides of high valent iron, mixed acid etching can be used, which not only plays the tearing role of hydrogen on the oxide scale, but also accelerates the chemical dissolution of its oxides.However, if there are only loose corrosion products (mainly Fe2O3) on the metal surface, it can be etched with hydrochloric acid alone, because it has fast etching speed, less matrix dissolution and less hydrogen permeation.
However, when the metal surface is a tight oxide skin, the consumption of hydrochloric acid alone is large and the cost is high. At the same time, the stripping effect on the oxide skin is worse than that of sulfuric acid.
Electrolytic etching (electrolytic acid, electrochemical etching) can be carried out in 5% ~ 20% sulfuric acid solution whether cathodic electrolysis or anodic electrolysis PR electrolysis (periodic change of workpiece positive and negative electrode electrolysis).
Compared with chemical etching, electrolytic etching is easier to quickly remove the firmly bonded oxide scale, has less corrosion to the base metal, and is easy to operate and manage. It is suitable for the automatic electroplating line.PR electrolysis is widely used to remove stainless steel scale in Japan.
In China, electrolytic pickling of cathode and anode combined with electrolytic degreasing is used for pretreatment of plating.Ferrous metal anode electrolytic acid is suitable for processing a large number of metal parts with oxide scale and rust. It can be carried out at room temperature. Increasing the temperature can improve the acid etching speed, but it is not as large as chemical acid etching. The current density increases and the acid etching speed increases. However, when it is too high, the base metal will be passivated.
At this time, the chemical and electrochemical dissolution of the base metal basically disappeared, leaving only the stripping effect of oxygen on the oxide scale.Therefore, the increase of etching speed is very small, which must be good at mastering its characteristics. Generally, the current density of 5 ~ 10A / DM2 is appropriate.For anodic acid etching, o-xylene thiourea or sulfonated wood glue can be used as corrosion inhibitor, and the dosage is 3 ~ 5g / L;Ferrous metal cathode electrolytic acid can be sulfuric acid solution or mixed acid of sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid of about 5% each, plus an appropriate amount of sodium chloride. Because it has no obvious chemical and electrochemical dissolution process of metal matrix (iron), proper addition of compounds containing Cl – can help loosen the oxide scale on the surface of parts and accelerate the etching speed,At the same time, formaldehyde or Urotropine can be used as corrosion inhibitor.
In short, sulfuric acid is widely used in acid etching of steel, copper and brass.In addition to the above, sulfuric acid, together with chromic acid and dichromate, is used as aluminum deoxidizing and de hanging agent.
It is used to remove stainless steel scale with hydrofluoric acid or nitric acid or both.The advantage of hydrochloric acid is that it can effectively pickle many metals at room temperature. One of its disadvantages is that attention must be paid to the prevention and control of HCl vapor acid mist pollution.
In addition, nitric acid and phosphoric acid are also commonly used for manual plating pretreatment.Nitric acid is an important component of many bright etchants.It is mixed with hydrofluoric acid and applied to the removal of heat-treated oxide scale on aluminum, stainless steel, nickel based and iron-based alloys, titanium, zirconium and some cobalt based alloys.
Phosphoric acid is used for rust removal of steel parts. It can also be used in special bath liquids of stainless steel, aluminum, brass and copper.Phosphoric acid nitric acid acetic acid mixed acid is used for the pretreatment of bright anodization of aluminum parts. Fluoroboric acid has proved to be the most effective acid lotion for lead based alloy or copper or brass parts with tin welding.
It is reported that the removal of metal oxide scale and oxide consumes 5% of the world’s sulfuric acid output, 25% of hydrochloric acid, most hydrofluoric acid and a large amount of nitric acid and phosphoric acid.
Therefore, correctly mastering these acids for acid etching is obviously an important topic in the application technology of pre plating treatment, but it is not difficult to use them, and it is not easy to use them well, save use and reduce consumption.
The degreasing and etching processes described above are the pretreatment processes commonly used by urban and rural electroplating manufacturers in China. These processes are undoubtedly effective.
Therefore, it is of great practical significance to further study and improve the application technology.However, from the perspective of development, it must be recognized that these processes still have some shortcomings that need to be improved:
① Chemical or electrolytic degreasing and etching all need to consume a lot of electric energy and heat energy.
For China, where the contradiction between energy supply and demand is becoming more and more prominent, energy conservation is an urgent problem to be solved in the current enterprise reform.
It is estimated that a medium-sized decorative Ni Cr Electroplating straight-line automatic line only consumes electric energy for electrochemical degreasing removal, accounting for about 20% of the total power consumption of the whole line.
In addition, the thermal energy consumption of temperature rise and insulation (steam heating) for chemical and electrolytic degreasing removal accounts for 40% ~ 80% of the total thermal energy of the whole line;
② There are many factors affecting degreasing removal and etching, especially for plated parts with complex geometry;
③ Increase power supply equipment, heating pipes, bdegreasinger coal consumption and air extraction equipment. In addition, there are many pretreatment baths, large floor area, high energy consumption and difficult maintenance. If there is a little mismanagement, alkali fog and acid fog will pollute the environment and affect the quality.
In recent years, with the development of China’s economic reform, energy-saving science and electroplating technology, many metal cleaning agents that can replace gasoline cleaning, as well as various energy-saving degreasing and derusting cleaning agents and corrosion and fog inhibiting additives have emerged in the market.The emergence of these new products and the new one-step process of degreasing and rust removal soon showed their vitality in application.
Their common characteristics are low or normal temperature, good static energy-saving effect, safety and non-toxic.At present, many domestic manufacturers are also constantly introducing and exploring advanced processes and cleaning agents for pretreatment, such as degreasing and rust removal. Obviously, this is a gratifying development trend.
How to apply it in continuous exploration?
Our experience should pay attention to mastering the pretreatment of manual production line. Due to the flexible operation sequence, we can decide whether to choose or not according to the specific situation at any time.
Because its strain capacity is stronger than that of automatic line electroplating, it can not be mechanically applied to automatic line. Because a new process and new cleaning agent are used in automatic line, many problems must be demonstrated repeatedly, otherwise being eager for success will cause mass losses.
However, new cleaning agents that can save energy and reduce consumption can be gradually adopted, which can be appropriately replaced first, and the primary electrolytic degreasing removal can be retained, and then gradually improved.In addition, during the trial use of the above new products, due to the mechanical restrictions on the action of the automatic line, strict requirements must be made on the defoaming and cleaning performance of the cleaning agent in the application, so as to prevent faults caused by carrying and polluting the electroplating bath solution.
In addition, the degreasing and rust removal time shall not be too long, and the operation and cost must be considered.
In short, the development of these new pretreatment processes and cleaning agents for the purpose of energy saving and consumption reduction is undoubtedly the direction of the current electroplating reform, which must be fully affirmed and adhered to.It is hoped that relevant scientific research, manufacturing and application units will cooperate horizontally, make great efforts in application technology, and strive to break a new path in pre plating treatment.
5.Study on the function and application technology of cleaning
After degreasing and etching, the residual solution and residual salt attached to the plated parts must be thoroughly washed or combined with neutralization and film removal measures to continuously and repeatedly clean the metal surface to reduce the surface tension and drag loss, so as to eliminate the electroplating fault in construction in the pre plating treatment.
However, washing the workpiece with water seems simple and not easy.The cleaning work should be scientific and reasonable, and can be closely coordinated with degreasing removal, etching neutralization and other processes, so as to not only improve the electroplating quality, but also save water, energy and consumption. There are many application technical problems worthy of study.
With the continuous development of electroplating production, how to reduce the carrying of bath liquid and strengthen the effectiveness of flushing through the improvement of cleaning method is an important link to ensure the anti-corrosion and decorative performance of coating.
At the same time, attention must be paid to reducing the amount of cleaning water as much as possible while ensuring that the workpiece is cleaned.
Different cleaning methods have different cleaning effects.For example, the water consumption of countercurrent rinsing is much less than that of other cleaning methods, which is conducive to the treatment of wastewater and the utilization of recycled water.Therefore, countercurrent rinsing is continuously promoted in electroplating production.However, attention should be paid to:
① Characteristics of multistage countercurrent rinsing in application.
The earliest cleaning method used in electroplating production is single bath cleaning. Multistage sectional cleaning can save a lot of water than single bath cleaning, but the number of baths increases, the floor area is large and the operation is complex. Multistage countercurrent rinsing improves the shortcomings of the former and saves more than 95% water than single bath cleaning.
Generally, three baths (stages) are used. Due to the low water consumption of three-stage countercurrent cleaning, it is easy to realize the idea of circulating and repeated water, and the waste water is discharged less or not, so as to achieve the purpose of “closed circulation”, which is conducive to electrolyte recovery and environmental protection.
② Multistage countercurrent rinsing production process.
Three stage cleaning is usually used.In order to overcome the uneven concentration in the bath caused by low water consumption and poor cleaning effect, degreasing-free compressed air or ultrasonic device are generally used.
The joint bath is used for cleaning, and the continuous water supply flow cleaning is generally used in the design.The inlet and outlet of the cleaning bath should pay attention to the water inlet from the lower part and the water outlet from the upper part, which can play a certain mixing role.
As for the size of the bath, while meeting the maximum electroplating parts and hangers of the unit can operate smoothly, pay attention to maintaining a high flow rate on the water surface and the renewal of cleaning water.
In addition, a baffle shall be added between the baths of the joint bath to prevent the water from overflowing into the adjacent baths due to the rise of water level during cleaning and affecting the cleaning quality.
Although there is no unified standard in China for the allowable range of dissolved substances and impurities in cleaning water, the highly toxic cyanide and hexavalent chromium should be strictly controlled according to the relevant process wastewater standards.
Therefore, the cleaning between two processes must not affect the quality of the next process.For cleaning before chromium plating in hydrochloric acid or after sulfuric acid, excessive Cl – and SO2-4 must be prevented from being brought into the chromium bath.
Therefore, it should be strictly controlled within the low content limit. For the cleaning after alkali washing and before acid etching, the content limit is wide, which can be between 1 ~ 3G / L.
Therefore, cleaning is an indispensable step in the electroplating process, and the current problem is that we must pay attention to the management improvement and improvement in this regard.
In short, improving and improving the pretreatment process and management is a work of strategic significance in the current electroplating reform.






 Nov. 09, 2021
Nov. 09, 2021