Metal materials are damaged by the action of surrounding media, known as metal corrosion, which is the most common form of corrosion. The corrosion effects of different metals in different environmental conditions are different. Generally, the usage environment of products can be roughly divided into three types: indoor environment, outdoor environment, and marine climate environment.
(1) Indoor environment: The main factor that corrodes metals in the air is mostly oxygen. However, significant actual corrosion occurs only when the air has a certain relative humidity (i.e. critical humidity). The general critical humidity is 60% to 70%, and the greater the critical humidity, the greater the corrosion effect.
In living and working rooms, the relative humidity is high in summer, so the corrosion effect is greater than in winter. In mountainous and marine areas, the relative humidity indoors is mostly higher than in flat inland areas, and the corrosion effect is relatively significant. If there are no particularly corrosive components in the air, the amount of corrosion is generally relatively small. Therefore, the corrosion effect will be exacerbated by the increase of dust, gaseous impurities in the air, especially sulfur dioxide, acid mist (organic compounds containing eight sulfur compounds produced by combustion gases), and the increase of eight ammonia gas (mainly in toilets and woodworking yards) in kitchens and dining rooms.
More severe corrosion may occur due to contact between the workpiece and various objects, such as sweat, wood (organic acids or wetting agents), paper (acids, alkalis, chlorides, and sulfides), etc.
(2) Outdoor environment: The impact of corrosion is basically similar to that of indoor environment, with the main difference being that outdoor environment mostly contains more impurities and atmospheric dust.
Rainwater, on the one hand, wets metals, thereby promoting corrosion; On the other hand, it may also accelerate the flushing of corrosive components, thereby reducing the corrosion effect.
The main corrosion factors in outdoor environments originate from flue gas, which increases the content of sulfides in the air, especially sulfur dioxide, sulfuric acid, and ammonium sulfate. Therefore, atmospheric corrosion is generally greater in industrial areas than in urban areas, and urban areas are also greater than in rural areas. In residential areas, the sulfur content in the air in winter is mostly significantly higher than in summer.
(3) Marine climate environment: On the coast, most areas have high relative humidity (above 80 ^) and high salt content, which promotes enhanced corrosion. But the corrosion hazard zone is only a few thousand miles wide along the coast, and there are significant differences within this area. If an object is directly subjected to the action of fine water mist particles in the seawater area, the corrosion effect will also accelerate.
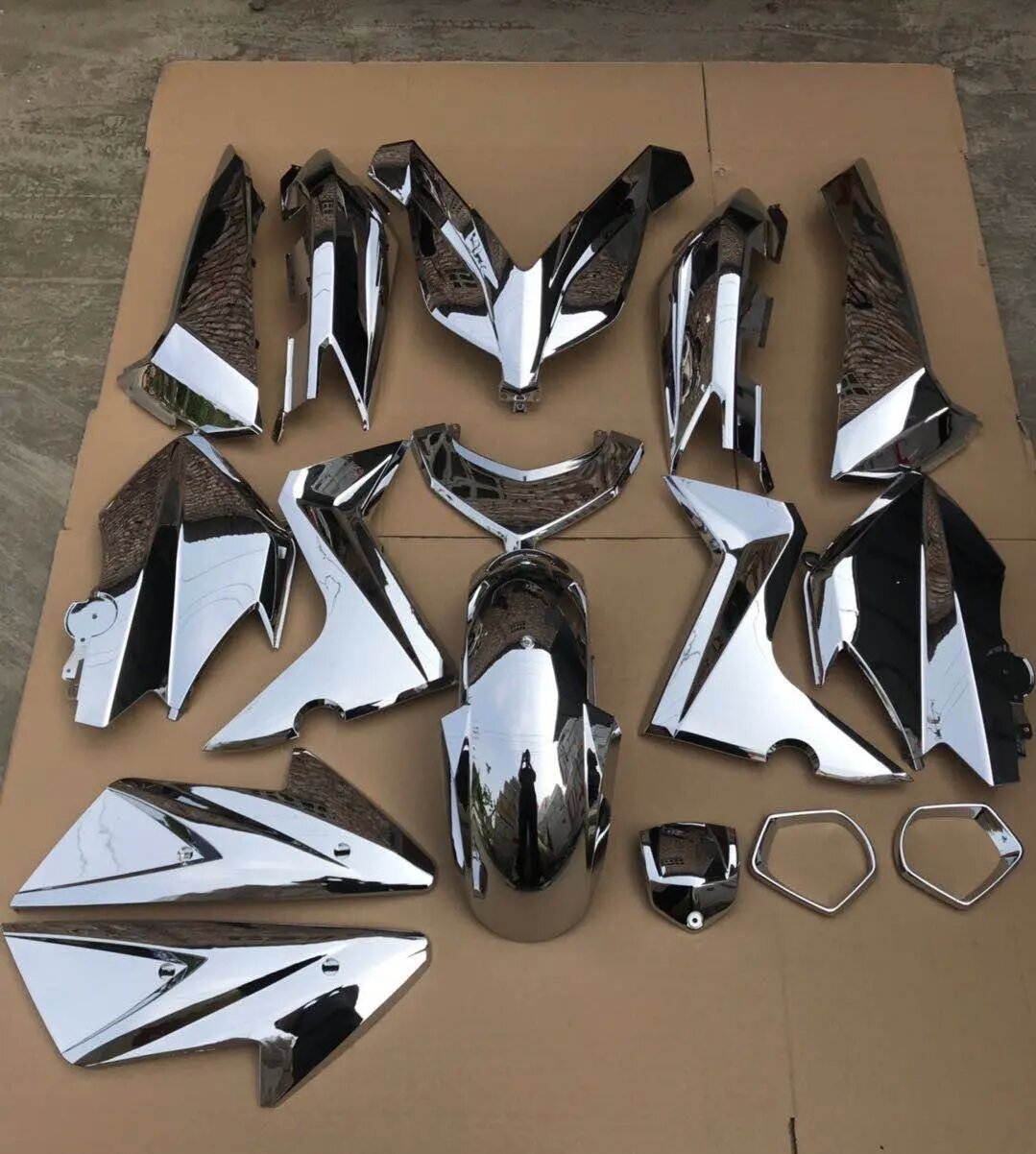
In order to overcome the phenomenon of metal corrosion in daily life and production, people have adopted some metal surface treatment methods to prevent metal corrosion – electroplating. Electroplating is a process that uses electrolysis to attach a layer of metal film to the surface of a metal, thereby preventing metal corrosion and improving its hardness, wear resistance, and conductivity.






 Dec. 21, 2023
Dec. 21, 2023