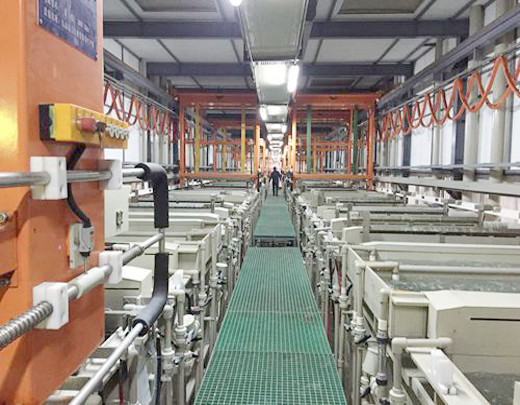
For electroplating, the heating temperature of electroplating solution is very important. Different electroplating (anode) materials and electroplating solution have different temperature requirements. Incorrect heating temperature will affect the electroplating production efficiency and product quality.
1. The plating species requiring heating
– Zinc nickel: 18-22 degrees
– Watt nickel: 55-60 degrees
– Semi bright nickel: 55-65 degrees
– Bright nickel: 55-65 degrees
– Nickel seal: 55-65 degrees
– Hard chromium plating: 52-58 degrees
– Decorative chromium plating: 30-35 degrees
– Alkali Zinc: 18-22 degrees
– Acid zinc: 20-25 degrees
– Acid copper: 18-20 degrees
– Chemical nickel (high temperature alkaline): 30-40 degrees
– Chemical nickel (high temperature acidic): 85-95 degrees
Heating mode
1) Tubular heating (stainless steel pipe, titanium pipe, seamless steel pipe, etc.), heat source – steam
2) Tubular heating (stainless steel pipe, titanium pipe, Teflon, PTFE, etc.), heat source – electricity
3) Water heating, heat source – steam, electricity
Heating purpose
1) Ensure that the bath temperature is within the range of electroplating parameters.
2) Improve current efficiency
2. The plating species requiring cooling
– Rolling galvanized nickel
– Hanging galvanized nickel
– Acid copper
– Acid zinc
– Alkali zinc and Chromium plating.
There are generally two cooling methods.
– Tubular direct drop: The tank liquid is cooled directly through the chiller.
– Tubular water drop: The chiller cools the cooling water first, and the low-temperature cooling water circulates through the pipeline to reduce the tank liquid temperature).
Cooling purpose
If the bath temperature is too high, the coating is easy to scorch or even cannot be plated.






 Dec. 20, 2019
Dec. 20, 2019